Wondering what’s the verdict on the data product manager vs product manager debate?
Developing a product that customers fall in love with is a challenging task. It requires experience, experimentation, skills, data, and much more to create a powerful product. A product manager is the main person who is responsible for product success. A product manager has the potential to increase company profits by 34.2% by optimizing product management.
This guide covers the key differences between data product managers and product managers. It identifies similarities and differences between the two roles.
To learn more via video, watch below. Otherwise, skip ahead.
Data Product Manager vs Product Manager
Data product managers and product managers are two overlapping roles that have a lot of similarities in terms of responsibilities, skills, and entry requirements. At the same time, there are several key factors that differentiate both roles.
Let’s take a closer look at these differences by breaking down the roles and responsibilities of each job position.
Who is a Product Manager?
A product manager (PM) is responsible for product success. They are the persons who identify customer needs and then develop a strategy and roadmap for product development. The role of a product manager is diverse and spans everything from product design and development to marketing and sales.
A product manager ensures product development (including features and UX), handles end-to-end product management, and does everything to come up with a product that exceeds user expectations.
Who is a Data Product Manager?
A data product manager is the data science version of a normal product manager. They are responsible for managing data and data flow throughout the product life cycle.
It is therefore the responsibility of the data product manager to develop a data-driven product and its features that adhere to the organization’s vision and user expectations.
Data product managers deal with everything related to data, data science teams, and data products right from strategy to implementation and execution and beyond.
Data Product Manager vs Product Manager: Key Responsibilities
Data is the key differentiator between a data product manager and a product manager. It isn’t that a PM doesn’t have to manage and deal with data; rather, there is a difference in the scope, scale, and mindset of data usage of a PM as opposed to that of a data PM.
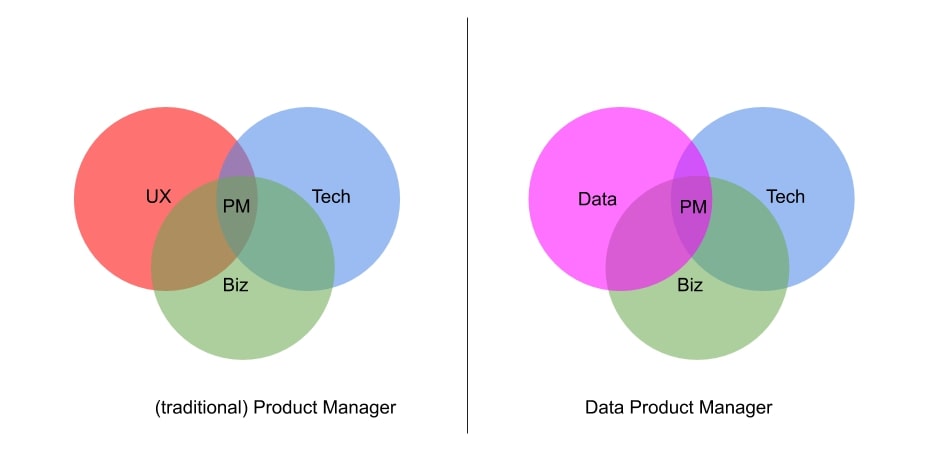
Credits: Medium
A data PM uses data and experimentation for decision-making related to product development and management. Management of data is the primary responsibility of a data PM. This takes into account the creation, storage, organization, and flow of data.
The major responsibilities and key data product manager role include:
- Using data for product development and data management
- Collecting, storing, organizing, and analyzing data
- Managing a data science team, machine learning algorithms, and data engineers
- Optimization of UX and CX based on available data
- Data warehousing and pipeline strategy development
- Data-driven product development, management, and experimentation decision-making.
On the other hand, while PMs leverage data in some way, shape, or form, it is not their primary responsibility or specialization. The main responsibilities of a PM include:
- Defining product vision and story
- Conducting market research and competitive analysis
- Understanding user needs and developing product feature
- Identifying and prioritizing product management tasks
- Collaborating with other teams including engineering, marketing, sales, tech, and more to ensure seamless UX and customer satisfaction.
Certifications
You need certifications to master and excel as a big data product manager and PM. The job you are applying for might not require certifications but having certifications enhances your chances of landing a job.
Picking the right certification is essential.
Looking for product management certification? Consider our Product HQ Certified Product Management Courses in data PM, technical PM, and traditional PM to equip yourself with the knowledge you need to succeed in the field.

Skills
The skills you need to become a data product manager are different from what you need to become a successful PM. This is because one is more focused on data while the other is more customer-centric.
Here is the list of the skills a data product manager should have:
- Product management
- Data science and machine learning algorithms
- Big data and data analytics
- Business intelligence
- Communication skill
- Data analysis and management
- Data product development
- Understanding of data lifecycle
- Understanding of machine learning, statistics, SQL, and data analysis and management tools and techniques.
And here are the key skills that a conventional product manager needs:
- Communication skill
- Business skills
- Technical expertise related to UX
- Research skills
- Analytical skills
- Critical thinking and decision-making
- Marketing and management skills.
Salary
How much is the average salary a data PM or PM pulls in every year?
The average salary of data product managers is $116,036 per year in the US, according to Glassdoor.
Talent estimates the average salary of data product managers in the USA (based on 1028 studies) to be $136,580 per year.
Meanwhile, Indeed reports that the average yearly salary of a PM in the USA is $90,202 based on 4.1K salaries. New York is the state with the highest salary for product managers (18% higher than average).
According to Talent, the average salary of a PM in the USA is $110,318 per year (based on 1,000 salaries).
The difference between the salaries isn’t significant. That said, data product managers earn more than conventional product managers because they possess additional skills relevant to data management, data analytics, and data-driven products.
Career Path
The career path of both data PM and conventional PM is similar. As a data PM, you need to take on a role to become a senior product manager and then move towards director-level.

Credits: Zippia
One becomes a product management director, senior director of marketing, or vice president after 12 years of experience. One also has the option of pursuing a more senior position in data and analytics after serving as a data-driven product manager in any organization.
As a PM, you have several exciting leadership roles that you can pursue as you move ahead. One option is to climb up the corporate ladder and become a product director or chief product officer. If you decide to switch careers, you have the option of transitioning into brand management and climbing up the ladder in that profession.
Data Product Manager vs Product Manager: Takeaways
Most organizations choose between either a data product manager or a traditional product manager when hiring someone for product management.
However, large organizations with diverse product portfolios need both data PM and conventional PMs depending on the types of products they have. In such cases, the data PM and PM work together.
Their responsibilities vary from organization to organization but the data PM manages data and all the products that are data-driven while the product manager looks after traditional products and their UX.
While their specialized areas are different, their responsibilities overlap. This makes it easier for them to work together for the betterment of the product’s success at every stage of its lifecycle.
