Are you in search of the fundamental skills for becoming a Scrum manager? Then look no further.
The rise of the Scrum project management framework dates back to the year 1995. Jeff Sutherland and Ken Schwaber, two original signatories of the Agile Manifesto, introduced this framework which centers on three pillars; transparency, inspection, and adaptation.
Becoming an effective Scrum master requires a thorough understanding of the agile Scrum principles and Scrum values that govern Scrum team productivity.
This article serves as a guide to the essential skills that are in demand for Scrum master jobs.
Top 5 Scrum Manager Skills
Let’s dive right in.
1. Communication Skills
In any leadership position, effective communication is a transferable skill that helps to support teams and encourage feedback and innovation.
Within the Scrum master role, communication skills are vital. This is because Scrum masters collaborate with the product owner and Scrum teams to ensure that they all comply with Scrum methodologies and complete iterations without any obstacles.
For the Scrum master, communication skills encompass both verbal and written communication. Technical writing is necessary for providing updates to product owners and senior management alike.
Facilitate Meetings
One aspect of Scrum project management is the daily Scrum meeting. These are stand-up meetings with a duration of no more than 15 minutes, where the entire team has the opportunity to assess their progress.
To keep daily Scrum meetings brief and efficient, team members respond to the following questions:
- What tasks did you complete yesterday?
- What tasks are on schedule for completion today?
- Are there any factors hindering your progress?
The intent is to measure how much time each team member needs to complete tasks. The Scrum master must keep track of the team’s progress while making a note of any obstacles that prevent them from remaining on schedule.
The Scrum master ensures that the daily meetings are on time and productive while ensuring that all team members, including those who do remote work, are in attendance and active participants in the daily meetings.
Conflict Resolution
Product development is a dynamic and complex field of work that requires input from several individuals with varying ideas, personalities, and work styles. This means that internal conflicts arise on occasion.
It is, therefore, the responsibility of the Scrum master to identify and resolve these situations so that they do not hurt the team’s progress. Being a Scrum master necessitates having the skill set to navigate through conflicts and find solutions that benefit all parties.
Some strategies for conflict resolution include:
- Avoiding: ignoring the existence of conflict altogether
- Competing: where one party asserts their victory over the dispute
- Accommodating: where one party is willing to submit to the wishes of another
- Collaborating: each party makes contributions toward finding a solution
- Compromising: each party arrives at a mutual agreement
Mentoring
One of the primary functions of a Scrum master is to ensure that everyone on the team operates according to the same agile practices and principles. Therefore, strong teaching and mentoring abilities are vital, in particular when working with teams who are new to the agile environment and Scrum processes.
It is essential that Scrum masters not only have knowledge of what to do in these instances but also can explain how to proceed and why it is necessary to do so. This approach to team coaching encourages Scrum teams to improve their technical and collaboration skills to maximize potential and output.
In the end, Scrum team members become confident in their roles and gain a sense of project ownership and independence.
Looking to become a scrum master? Enroll in our top-rated certification courses to do just that:
2. Technical Skills
As a Scrum master, having the requisite technical skills, such as software design and development, programming, and process integration, to name a few, is beneficial to the fulfillment of this role.
There are numerous frameworks to choose from that help develop these technical skills. An example of this is Kanban which also aligns with Scrum methodology, making it a useful tool for Scrum planning, execution, and overall Scrum project management.
These technical skills allow Scrum masters to build programs that encounter minimal roadblocks during the software development process. For the aspiring Scrum master, it is advantageous to undergo further training through the certified scrum master and certification courses.
Project Management Tools
The use of project management tools and resources is essential to Scrum master jobs. These development tools help to master key skills, such as budget planning and allocation, feasibility testing, generating reports for senior management, and managing multiple projects and teams.
One of the key project management tools for Scrum masters is the task board. Task boards are visual representations of the user stories or work that a Scrum team has in progress. It allows Scrum teams to track, organize, and manage their workflows. An example of this is the Kanban board.
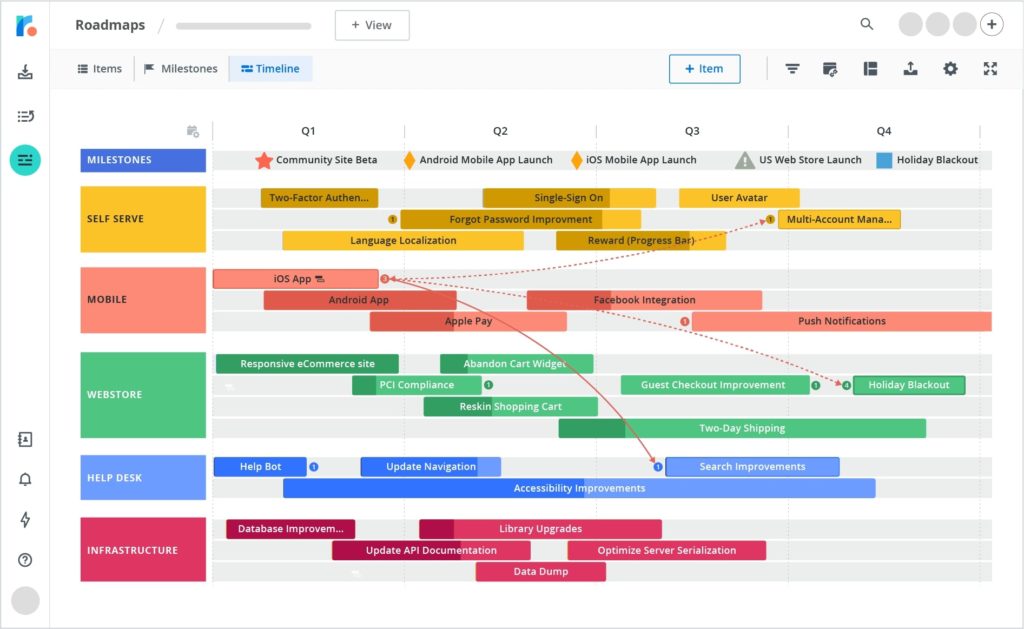
Credits: Roadmunk
The Scrum master is responsible for setting up the task board ensuring that team members are aware of their tasks and the requirements for completion. In addition to setting up the task board, the Scrum master must create guidelines for efficient use and communication about the task board.
Agile Software Development Knowledge
The Scrum methodology works in conjunction with agile principles, and as such, the purpose of the Scrum master is to ensure that teams function in keeping with these principles for software development.
Scrum masters are knowledgeable of the terminologies that exist within the Scrum framework that make the distinction between Scrum values and other frameworks such as Agile and Kanban. However, the Scrum master can drive the scrum team’s progress by teaching them how to adopt an agile mindset, which often encourages continuous learning and iterative production.
Software development that occurs by the Scrum methodology does, by default, enforce agile techniques.
3. Scrum Management Expertise
Previous work experience and educational background in project management are beneficial for the Scrum master job. The focal point in Scrum management is facilitating the exchange of information across both the Scrum team and project team so that they prioritize self-organization and adaptability.
Scrum Knowledge
Scrum masters use their understanding of the core principles of Scrum methodology to drive the execution, adaptation, and testing of software designs. Leading the Scrum team also requires knowledge of the other components that Scrum teams perform regularly. Scrum ceremonies or scrum events. Scrum masters are responsible for conducting these meetings.
These Scrum artifacts and events help to regulate project management processes and are inclusive of the following:
- Product Backlog
- Product Increment
- Sprint Planning
- Sprint Review
- Sprint Retrospective
- Sprint Burndown Chart
- Definition of Done
Servant Leadership
A top Scrum master leads by example. Rather than just focusing on their duties, they consider the needs of the entire team to ensure that everyone has a fair chance at fulfilling their duties.
It is important that Scrum masters function as both the leader and a member of the team. Servant leadership helps to motivate teams and encourage group cohesion. In achieving this, Scrum masters foster healthy relationships and serve as the link between leading agile teams, the development team, and the product owner.
Since the product owner creates user stories and the development team works to prioritize them, the Scrum master ensures these elements coincide. If the product owner makes changes to the backlog, the Scrum master takes the lead in informing the team about the product changes, in particular when changes have the potential to affect work in progress.
4. Administrative Skills
The Scrum master role requires administrative skills that aim to increase productivity throughout the software development process.
Organizational Skills
Scrum masters manage multiple deadlines throughout sprint planning and execution. As such, organizational skills are essential to this position as it plays a pivotal role in task assignments, scheduling Scrum meetings, and making note of changes during each sprint cycle.
The success of Scrum teams depends on prioritizing tasks and upholding the Scrum framework to which team members adhere. Organizational skills also encompass ensuring that teams maintain favorable communication and stay on track with their schedules.
To achieve this, Scrum masters establish a team agreement. This is a document that outlines a series of team requirements such as operating hours, Scrum ceremony structures, escalation paths, and involvement of key stakeholders. The intent is to foster transparency across the development team.
Interpersonal Skills
A Scrum master’s success when working with software development teams, programmers, and technicians alike, is indicative of their interpersonal skills. Building relationships within the workplace, understanding the workstyles of team members, and encouraging open communication are essential Scrum master skills.
Doing this motivates Scrum teams to perform at optimal levels and collaborate to achieve sprint goals.
Onboarding
Since the Scrum master role involves mentorship, it is within their scope of work to onboard new employees by introducing them to the Scrum methodologies to ensure that development teams maintain efficiency during the sprint.
A great Scrum master uses mentoring opportunities to assist new team members with understanding the product vision and Scrum framework to guarantee adherence to the methodology, thus driving productivity.
The intent is not to manage but to train the development team to the extent that they become independent and accept accountability for project outcomes.
5. Strategy and Execution
The Scrum process requires Scrum masters to develop a strategic mindset. This mindset sets the pace for the creation of an effective strategy that allows for efficiency when completing tasks which, in the end, impacts the business goals and solidifies the Scrum master role within the company.
Teamwork and Collaboration
The Scrum master is, in essence, a team leader because the success of the Scrum framework is dependent upon their guidance. Teams then use this knowledge to become self-managing and collaborative to produce high-value deliverables.
When Scrum teams become self-sufficient, they do not require constant supervision from the team leader. Instead, team members work together to complete sprints as well as resolve any internal conflicts that arise.
This culture of team collaboration within the organization is vital to project management success.
Risk Management
One of the key Scrum master skills is managing risks, that is, identifying, mitigating, and monitoring them. Effective risk management permits teams to maintain an efficient workflow and provide value during every iteration.
During software development, it is not uncommon for hindrances to occur. While these stem from technical or administrative issues, to name a few, they result in risks that impact the quality of deliverables and even customer experience.
A scrum master works to identify these risks and works in conjunction with software developers to evaluate, rank, and communicate them to the product owner and key stakeholders to determine how to proceed with mitigation.
Remove Roadblocks
The Scrum masterworks to identify roadblocks or distractions that hinder progress during each iteration.
Roadblocks occur in different ways and range from too many irrelevant meetings to too many assignments. The purpose of the Scrum master in these instances is to liaise with the product owner, stakeholders, and other team members to regulate meeting attendance and divide the workload.
Keep in mind that each roadblock is unique and requires solutions that are tailored to the needs of each one.
Essential Scrum Manager Skills: Key Takeaways
A Scrum master helps with implementing these agile development methodologies across multiple teams within the organization. To do so, they put into practice numerous Scrum master skills that have a positive impact on how teams approach how they develop software.
Leadership skills are at the top of the list of essential skills, because the Scrum master is, after all, a servant leader who doesn’t just guide the team, but takes on an active role in contributing to sprint planning, and project management. Administrative, technical, and Scrum management knowledge, as well as a strategic mindset, are key contributors to becoming a Scrum master.
Scrum masters also possess strong verbal and written communication skills, which they utilize to guide the Scrum team to the point of self-sufficiency. This encourages creative ideas among teams and fosters team collaboration. Overall, Scrum is a simple framework that makes managing complex projects achievable.
FAQs
Here are answers to the questions about scrum and scrum management:
What does a Scrum manager do?
A Scrum Manager, often referred to as a Scrum Master, facilitates the Scrum process within a team. Their primary focus is on coaching the team to self-organize and achieve their sprint goals. They ensure that Scrum practices are followed, remove obstacles that impede progress, and help the team improve productivity and efficiency.
What are the top 5 qualities of a Scrum Master?
Here are the top five qualities of a good scrum master:
- Prioritizes the needs of the team and facilitates their success with facilitation skills
- Quickly identifies and resolves issues that hinder team progress.
- Conveys information and actively listens to team members.
- Understands and respects team members’ perspectives and fosters a supportive environment.
- Adjusts strategies and processes to fit the team’s needs and changing circumstances.
What are the skills required for a Scrum Master?
The hard and soft skills required for a successful scrum Master include:
- Strong facilitation and coaching abilities
- Effective communication
- Conflict resolution
- Scrum alliance
- Proficiency in Scrum practices and principles
- Ability to foster collaboration and teamwork
- Solid understanding of Agile methodologies
- Organizational skills
What are the hard skills in Scrum?
Hard skills in Scrum include:
- Proficiency in Agile project management tools like Jira or Trello
- Expertise in task and backlog management
- Knowledge of Scrum frameworks and methodologies
- Familiarity with metrics and reporting to track team performance
- Understanding of software development processes
If you are new to product management and are looking to break into your first product role, we recommend taking our Product Management Certification Courses, where you will learn the fundamentals of product management, launch your product, and get on the fast track toward landing your first product job.
